Understanding PCOS: Symptoms, Insulin Resistance, and Treatments
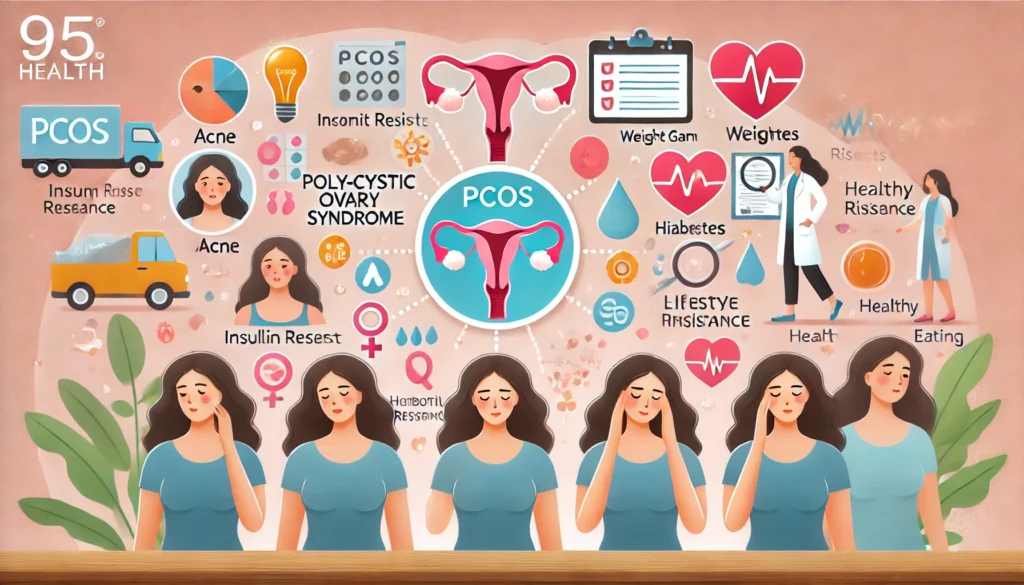
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting many women of reproductive age. It is characterized by a range of symptoms and often leads to complications such as insulin resistance, which significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Key Factors in Understanding PCOS
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance | A common feature in PCOS where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, leading to increased risk of type 2 diabetes. |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Excess androgens (male hormones) can cause symptoms like acne, hair growth, and irregular periods. |
| Genetics | Family history may increase the likelihood of developing PCOS. |
| Inflammation | Chronic inflammation is common in women with PCOS and can contribute to insulin resistance. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Diet, exercise, and weight management can significantly impact the management of PCOS symptoms. |
| Associated Health Risks | Increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea, and mental health issues like depression and anxiety. |
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a condition where multiple small, fluid-filled sacs (cysts) develop on the ovaries. These cysts result from hormonal imbalances, particularly an excess of androgens (male hormones) in women. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but factors such as genetics, insulin resistance, and inflammation are believed to play roles.
Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary widely among women, but some common signs include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles or absence of menstruation
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body (hirsutism)
- Severe acne and oily skin
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
- Thinning hair or male-pattern baldness
- Darkening of the skin, especially around the neck or under the breasts (acanthosis nigricans)
These symptoms often begin around the time of the first menstrual cycle but can develop later in life as well.

Insulin Resistance and PCOS
Insulin resistance is a key concern for women with PCOS. It occurs when the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. To compensate, the pancreas produces more insulin, which can lead to elevated blood sugar levels over time and eventually type 2 diabetes. Studies indicate that more than half of women with PCOS will develop diabetes or prediabetes before the age of 40.
Health Risks Associated with PCOS
Beyond reproductive issues, PCOS can lead to several serious health problems:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Due to insulin resistance, women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing diabetes.
- Heart Disease: Women with PCOS are more likely to have high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels, increasing their risk of heart disease.
- Sleep Apnea: This condition, where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, is more common in women with PCOS who are overweight.
- Depression and Anxiety: Mental health issues are prevalent among women with PCOS, though the exact cause of this link is still being studied.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing PCOS typically involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, blood tests to measure hormone levels, and ultrasounds to examine the ovaries.
While there is no cure for PCOS, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. Common treatment strategies include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss through a healthy diet and regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Medications: Birth control pills can regulate periods and reduce androgen levels, while medications like metformin can improve insulin resistance.
- Fertility Treatments: For women trying to conceive, treatments such as clomiphene or letrozole can induce ovulation.
Medicines for PCOS
| Medicine | Price & Availability |
|---|---|
| Metformin | $15 – $30/month Available at major pharmacies |
| Clomiphene Citrate | $20 – $50/cycle Available at major pharmacies |
| Spironolactone | $10 – $25/month Available at major pharmacies |
| Letrozole | $30 – $60/cycle Available at major pharmacies |
| Eflornithine Cream | $50 – $70/tube Available at major pharmacies |
Managing PCOS is an ongoing process, but with the right approach, women can control symptoms and improve their quality of life.
PCOS is a multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive management plan. By understanding the symptoms and associated health risks, women with PCOS can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being.
PCOS Awareness Quiz
Credits: 95health.com